Living
Marine Fungus Shows Promise in Tackling Ocean Plastic Pollution
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists have identified a marine fungus with the ability to break down polyethylene, a common plastic, when exposed to UV light. This revelation opens up new possibilities in the fight against ocean plastic pollution.
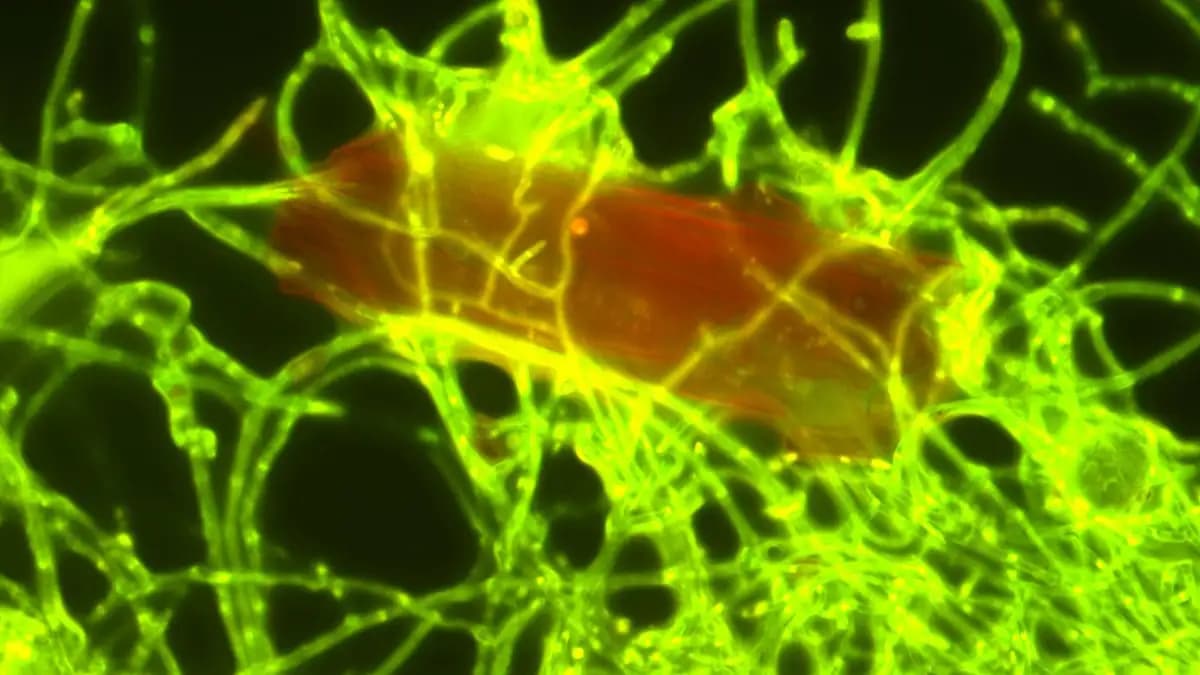
The marine fungus, Parengyodontium album, was found to degrade polyethylene after exposure to UV radiation, suggesting the presence of other plastic-degrading fungi in deeper ocean waters. Researchers, including those from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ), have shown that this fungus can break down plastic particles, adding to the limited list of known plastic-degrading marine fungi, which previously included only four species.
Parengyodontium album resides in thin layers on plastic debris, living alongside other marine microbes. The research, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, involved scientists from NIOZ, Utrecht University, the Ocean Cleanup Foundation, and various European research institutes. Their findings indicate that the fungus decomposes polyethylene (PE), the most prevalent plastic in the ocean, converting it primarily into carbon dioxide.
To accurately monitor the degradation process, researchers collected plastic debris from pollution hotspots in the North Pacific Ocean and isolated the fungus in a laboratory setting. They used specially labeled carbon isotopes to trace the carbon flow within the degradation products. “These so-called 13C isotopes remain traceable in the food chain. It is like a tag that enables us to follow where the carbon goes. We can then trace it in the degradation products,” explained lead author Annika Vaksmaa.
Vaksmaa expressed excitement over the quantifiable nature of this research, noting that the breakdown of PE by P. album occurs at a rate of approximately 0.05 percent per day. Interestingly, the fungus utilizes only a small fraction of the carbon from PE, excreting most of it as carbon dioxide. While CO2 is a greenhouse gas, the amount released by the fungus is comparable to what humans emit through respiration.
The study highlights the critical role of UV light in enabling the fungus to use PE as an energy source. “In the lab, P. album only breaks down PE that has been exposed to UV-light at least for a short period of time. That means that in the ocean, the fungus can only degrade plastic that has been floating near the surface initially,” Vaksmaa noted. This finding underscores the dual role of UV light in both mechanically and biologically breaking down plastic in marine environments.
Despite the promising potential of P. album, it is limited to degrading plastics near the ocean’s surface. Vaksmaa and her team believe other, yet-to-be-discovered fungi could be breaking down plastics in deeper waters. “Marine fungi can break down complex materials made of carbon. There are numerous amounts of marine fungi, so it is likely that in addition to the four species identified so far, other species also contribute to plastic degradation. There are still many questions about the dynamics of how plastic degradation takes place in deeper layers,” she said.
The urgency of finding plastic-degrading organisms cannot be overstated, given the staggering amounts of plastic produced annually—over 400 billion kilograms, with projections to triple by 2060. Much of this plastic ends up in the ocean, accumulating in subtropical gyres, where ring-shaped currents trap debris. The North Pacific Subtropical Gyre alone has collected approximately 80 million kilograms of floating plastic, illustrating the scale of the challenge.
Lead author Vaksmaa emphasized the significance of their discovery, noting the critical need for further research to uncover more plastic-degrading fungi and better understand the mechanisms of plastic breakdown in the ocean’s depths.
Living
Glasgow’s First Tree Hugging Tournament Aims to Bring People Closer to Nature
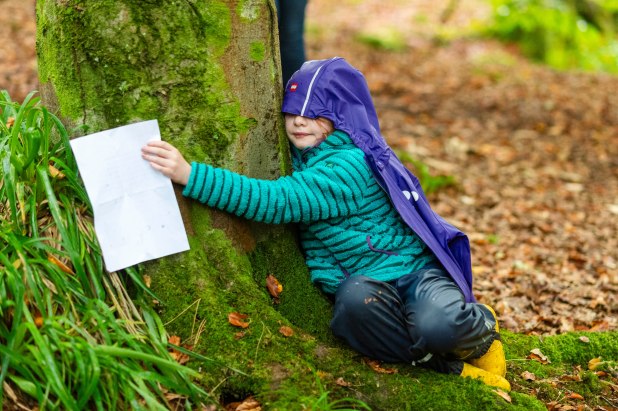

In a shady clearing at Dams to Darnley Country Park, Hannah Willow, barefoot and clutching twigs and leaves, gently approached a towering tree. After gracefully circling it, she wrapped her arms around its wide trunk, resting her cheek against the rough bark.
Willow, a 36-year-old teacher and children’s book author, was crowned the champion tree hugger at Glasgow’s inaugural Tree Hugging Tournament. The event, organized just outside the city, was designed to help people reconnect with nature in what organizers called a “playful and heartfelt way.”
“I’m over the moon,” Willow said, adorned with her leaf-and-branch crown. “I’ve always been a bit of a tree hugger, so being here with others who feel the same is wonderful. The woods are truly where I feel at peace.”
About 15 adults and four children participated in the event, which draws inspiration from Finland’s World Tree Hugging Championships. As the weekend’s champion, Willow earned a spot in the international competition, held in the HaliPuu forest, just north of the Arctic Circle.
The global competition was established in 2020 to lift spirits during the pandemic and encourage people to reduce stress by spending time in forests. Since then, similar events have sprouted worldwide, including Glasgow’s tournament and another in the Scottish Highlands.
Shuna Mercer, 50, and Vicki Dale, the organizers, emphasized the mental health benefits of nature. Mercer, an outdoor play therapist, explained, “We wanted to raise awareness about how vital it is to reconnect with the natural world. With so much time spent on screens, people are missing out on the emotional benefits that come from being outdoors.”
The tournament consisted of three rounds. In the first, participants competed in speed hugging, where they hugged as many trees as possible in one minute, ensuring each hug lasted at least five seconds. The second round, “dedicated” hugging, focused on showing deep connection and respect to a single tree. The final freestyle round allowed competitors to express their creativity through their most unique and personal tree hug.
Vicki Dale’s daughter, Lottie, won the children’s category. Wearing a pink raincoat and green boots, she set up a whimsical tea party with her teddy bear, Tom, and a gnarled tree, which she lovingly referred to as the “twirly tree.” Lottie also read a poem during the dedicated hug, saying, “I chose this tree because it stood out to me. It’s important for kids to connect with nature, and I love spending time in the woods with my mom.”
As for Willow, she’s now preparing to compete in Finland next summer. When asked for her advice on tree hugging, she shared, “It’s all about intention. Trees are living beings, just like us. When you give them a bit of love, it’s a beautiful thing.”
Living
Swiss Innovation: Revolutionizing Chocolate Production with Whole Cocoa Fruit
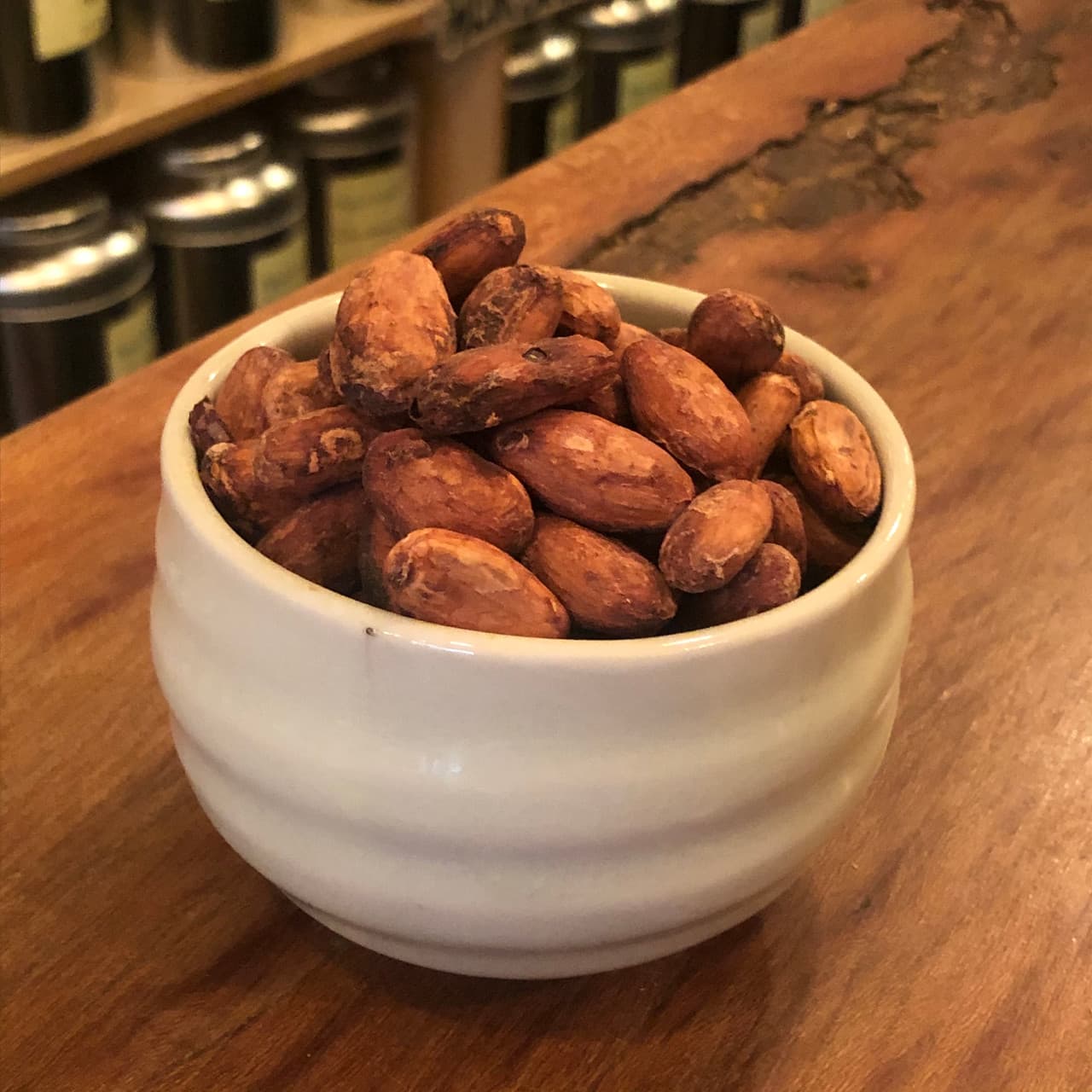

A groundbreaking development in chocolate production has emerged from Switzerland’s Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich. Food scientist Kim Mishra and his team have created a method to manufacture chocolate using the entire cocoa fruit, not just the beans, while eliminating the need for added sugar.
This innovative approach addresses several issues in the chocolate industry, including sustainability and farmer welfare. Traditionally, chocolate production discards most of the cocoa fruit, wasting valuable resources. The new method utilizes the fruit’s sweet juice, pulp, and even the husk to create a naturally sweet cocoa gel, potentially revolutionizing the industry.
The process has attracted attention from sustainable food companies and could solve multiple problems faced by the cocoa industry. Anian Schreiber, co-founder of KOA, a Swiss startup involved in the project, believes this approach could increase income for cocoa farmers and create more value in cocoa-producing countries.
This development comes at a time when the chocolate industry is under scrutiny for its historical links to colonialism and ongoing issues such as child labor and deforestation. The new method could contribute to more ethical and sustainable chocolate production.
The chocolate produced by this method has been described as having a rich, dark, yet sweet flavor with a hint of cocoa bitterness. However, challenges remain, including potentially higher production costs due to the current subsidies for sugar production.
Despite these hurdles, interest in the new method is growing. Chocolate producers from various cocoa-growing countries have reached out to learn more about the technique. Some major Swiss producers are beginning to incorporate more of the cocoa fruit in their processes, though none have yet eliminated sugar entirely.
As the Swiss chocolate industry, which produces 200,000 tonnes of chocolate annually worth an estimated $2 billion, looks to the future, this innovation could play a significant role in ensuring sustainability while maintaining Switzerland’s reputation for exceptional chocolate.
The development represents not just a potential shift in chocolate production, but also a step towards more sustainable and ethical practices in the food industry as a whole.
Living
Ukraine’s New Generation of Pet Owners: Finding Hope and Healing Through Animal Adoption

In the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, a heartening trend has emerged among the country’s younger generation. Millennials and Gen-Z Ukrainians, many of whom previously hesitated to take on the responsibility of pet ownership, are now stepping up to adopt animals displaced by the conflict. This wave of compassion is particularly evident in Kyiv, where the canine population now includes many furry friends with poignant wartime backstories.
This article highlights several touching tales of adoption:
Olena, a 30-year-old entrepreneur, found an instant connection with Chara, a dog rescued from Izium in the Kharkiv Region. Their bond formed quickly, creating a new family unit.
Daria, 31, welcomed Amelie, a cocker spaniel discovered near the Belarusian border by her boyfriend during a military mission. Amelie’s rescue fulfilled Daria’s long-held desire to help an animal in need.
Nastia, a 32-year-old designer with roots in conflict-affected regions, found solace in Spike, a mixed-breed dog from the Donetsk region. Their relationship has brought joy amidst Nastia’s experiences with displacement.
Vitalii, 33, and his wife Julia adopted Dyvo (meaning “Miracle” in Ukrainian), a puppy who overcame severe illness. For Vitalii, this marked his first deep connection with an animal, becoming a source of healing.
Costya, 34, and his girlfriend chose Runa from a shelter in Vasylkiv, appreciating the organization’s approach to reducing animal stress through temporary home placements.
Oleh and Lika, a creative couple, brought Maoshinda, a Ukrainian Laika, into their lives, overcoming initial hesitations about pet ownership.
Anya, 22, found companionship in Luna, a street dog who lost her puppies, filling a void left by wartime disruptions.
Max, 33, adopted Chief, a dog rescued from the Donetsk region, learning to navigate the challenges of pet ownership, including separation anxiety.
Olga and Andrii’s adoption of Sirko, a husky rescued from Irpin, prompted Olga’s return to Ukraine from Berlin, symbolizing a deeper commitment to their home during uncertain times.
These stories collectively illustrate how adopting animals affected by war has not only provided homes for displaced pets but also brought healing, purpose, and renewed hope to their human companions during a challenging period in Ukraine’s history.
Living
Breakthrough in Maugean Skate Conservation: First Captive-Born Hatchling Thrives
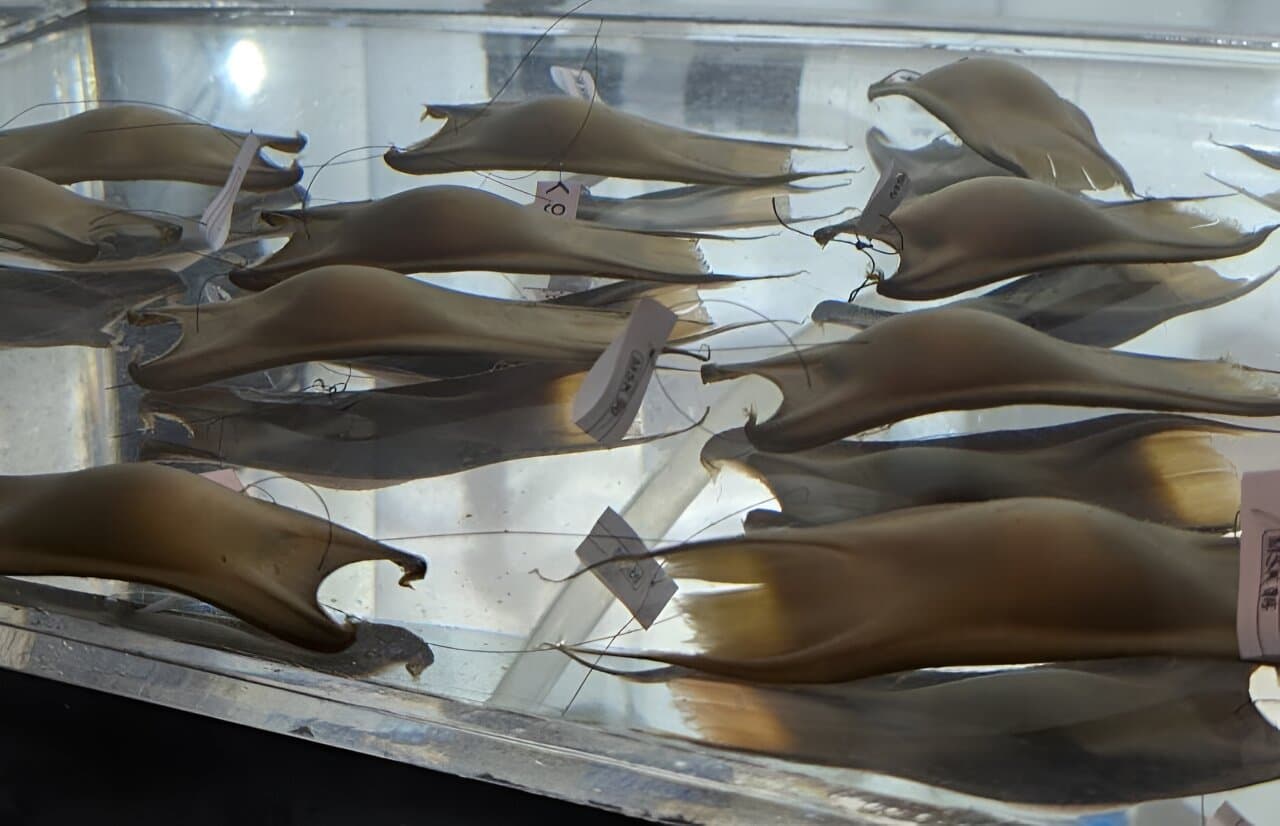

Scientists at the University of Tasmania’s Institute of Marine and Antarctic Studies (IMAS) are celebrating a significant milestone in their efforts to save the endangered Maugean skate. The captive breeding program, initiated in December, has produced its first hatchling from an egg laid in captivity.
Professor Jayson Semmens, who leads the project, expressed enthusiasm about this development, noting its importance in validating the program’s scientific approach. The success comes at a crucial time, as recent studies have shown a dramatic decline in the skate population in its last known habitat, Macquarie Harbour on Tasmania’s west coast.
The breeding program has seen remarkable progress since its inception. A female skate brought into captivity has been consistently producing eggs, with over 100 laid so far and about 70 showing signs of embryonic development. The first healthy female hatchling emerged on July 10, with more expected soon.
Interestingly, the eggs are being fertilized using sperm stored by the female from previous mating in the wild, as the captive male was initially kept separate to avoid disturbing the laying process. Scientists are now observing the interactions between the adult skates in captivity.
The program has evolved rapidly, moving from basic care of skates and their eggs to successfully nurturing embryos into viable hatchlings. While there have been challenges, including the loss of two adult skates early in the program, these setbacks have led to improved screening and care protocols.
Looking ahead, researchers are focusing on developing strategies for successfully reintroducing captive-bred skates into the wild. Macquarie Harbour’s unique environmental conditions, including naturally low oxygen levels, present specific challenges that need to be addressed.
The Tasmanian government has incorporated the captive breeding program into a broader conservation action plan for the Maugean skate. However, environmental groups stress the need for urgent attention to the root causes of the harbour’s poor water quality, particularly citing concerns about the impact of salmon farming.
Despite these challenges, the scientists involved in the project express a sense of privilege in their work to preserve this endangered species, viewing each day with the skates as a special opportunity to contribute to conservation efforts.
Living
Centennial Celebration: World Unites to Honor RAF Veteran with Flood of Birthday Wishes

A heartwarming global response marked the 100th birthday of Richard ‘Dick’ Skepper, a former Royal Air Force (RAF) serviceman. Following an appeal by the RAF Association, Skepper’s Warwickshire home was inundated with birthday cards from well-wishers worldwide, creating an unforgettable centennial celebration.
The outpouring of support left Skepper deeply moved. His son, David, shared that the cards came from an incredibly diverse range of senders, spanning multiple generations and continents. The family was amazed to see postmarks from as far as Australia and the Americas, alongside numerous European countries.
David emphasized how touched his father was by the thoughtfulness evident in each card. The veteran took the time to read every message, marveling at the variety of designs and their far-flung origins. While individual acknowledgment of each sender isn’t feasible, the family expressed profound gratitude for the joy these gestures brought to Skepper’s milestone birthday.
The centenarian’s military service began at 18 when he joined the RAF, eventually serving with 7 Squadron under Bomber Command at RAF Oakington in Cambridgeshire. His role as a Flight Mechanic – Engines (FM1) was crucial to the war effort.
To commemorate this special occasion, Skepper enjoyed a garden party at his nursing home, Kinton Manor, surrounded by loved ones. The global card-sending initiative not only honored his past service but also created new, cherished memories as he enters his second century of life.
This outpouring of international support demonstrates the enduring respect for veterans and the power of community to create meaningful celebrations across borders.
-

 OMG6 years ago
OMG6 years agoA Couple Gave Birth to the Most Beautiful Twins Ever
-

 OMG7 years ago
OMG7 years ago20 Rare Historical Photos
-

 OMG6 years ago
OMG6 years agoHilarious Airport Photos
-

 Cute6 years ago
Cute6 years agoMom Refuses to Let Daughter Eat Sugar and Years Later This is What She Grows Into
-

 OMG6 years ago
OMG6 years agoTop Secret Air Force One Facts That You Never Knew
-
OMG6 years ago
The Funniest Yearbook Photos Of All Time
-

 OMG6 years ago
OMG6 years agoRetired Mathematician Restores Log Cabin
-

 OMG5 years ago
OMG5 years agoWhat Happened When This ‘Duck Dynasty’ Legend Chopped Off His Beard?